Chapter 1. Seam Tutorial - JBoss Seam 1.0.0 正式版英文参考手册
In this tutorial, we'll assume that you have downloaded JBoss AS 4.0.4 and installed the EJB 3.0 profile (using the JBoss AS installer). You should also have a copy of Seam downloaded and extracted to a work directory.
The directory structure of each example in Seam follows this pattern:
Web pages, images and stylesheets may be found in examples/registration/view
Resources such as deployment descriptors and data import scripts may be found in examples/registration/resources
Java source code may be found in examples/registration/src
The Ant build script is examples/registration/build.xml
First, make sure you have Ant correctly installed, with $ANT_HOME and $JAVA_HOME set correctly. Next, make sure you set the location of your JBoss AS 4.0.4 installation in the build.properties file in the root folder of your Seam installation. If you haven't already done so, start JBoss AS now by typing bin/run.sh or bin/run.bat in the root directory of your JBoss installation.
Now, build and deploy the example by typing ant deploy in the examples/registration directory.
Try it out by accessing http://localhost:8080/seam-registration/ with your web browser.
First, make sure you have Ant correctly installed, with $ANT_HOME and $JAVA_HOME set correctly. Next, make sure you set the location of your Tomcat 5.5 installation in the build.properties file in the root folder of your Seam installation.
Now, build and deploy the example by typing ant deploy.tomcat in the examples/registration directory.
Finally, start Tomcat.
Try it out by accessing http://localhost:8080/jboss-seam-registration/ with your web browser.
When you deploy the example to Tomcat, any EJB3 components will run inside the JBoss Embeddable EJB3 container, a complete standalone EJB3 container environment.
The registration example is a fairly trivial application that lets a new user store his username, real name and password in the database. The example isn't intended to show off all of the cool functionality of Seam. However, it demonstrates the use of an EJB3 session bean as a JSF action listener, and basic configuration of Seam.
We'll go slowly, since we realize you might not yet be familiar with EJB 3.0.
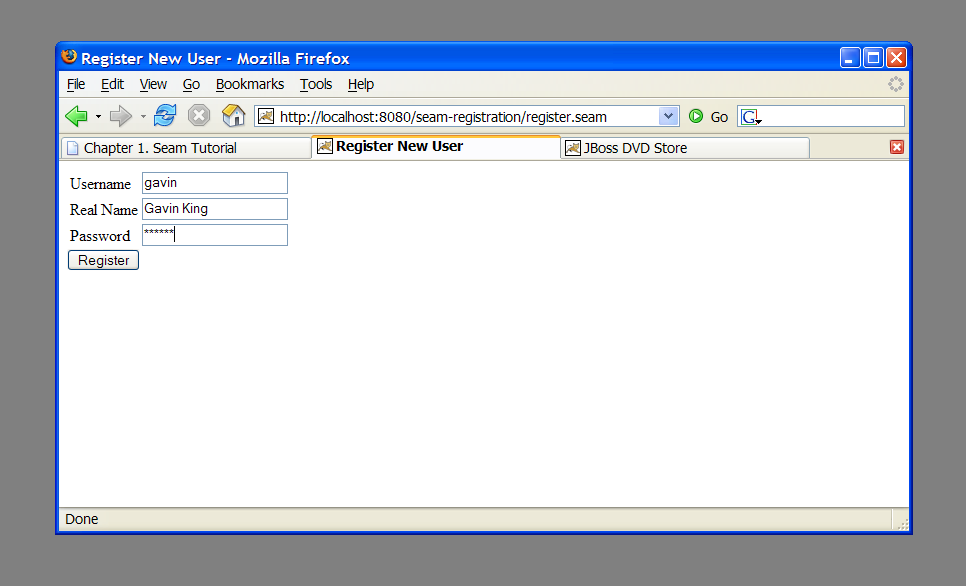
The start page displays a very basic form with three input fields. Try filling them in and then submitting the form. This will save a user object in the database.
The example is implemented with two JSP pages, one entity bean and one stateless session bean.
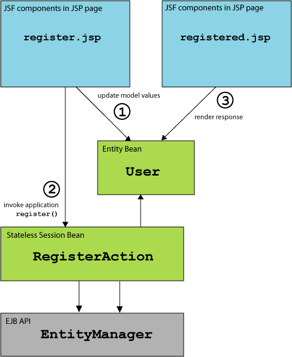
Let's take a look at the code, starting from the "bottom".
We need an EJB entity bean for user data. This class defines persistence and validation declaratively, via annotations. It also needs some extra annotations that define the class as a Seam component.
Example 1.1.
@Entity (1) @Name("user") (2) @Scope(SESSION) (3) @Table(name="users") (4) public class User implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1881413500711441951L; private String username; (5) private String password; private String name; public User(String name, String password, String username) { this.name = name; this.password = password; this.username = username; } public User() {} (6) @NotNull @Length(min=5, max=15) (7) public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } @NotNull public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Id @NotNull @Length(min=5, max=15) (8) public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } }
| (1) | The EJB3 standard @Entity annotation indicates that the User class is an entity bean. |
| (2) | A Seam component needs a component name specified by the @Name annotation. This name must be unique within the Seam application. When JSF asks Seam to resolve a context variable with a name that is the same as a Seam component name, and the context variable is currently undefined (null), Seam will instantiate that component, and bind the new instance to the context variable. In this case, Seam will instantiate a User the first time JSF encounters a variable named user. |
| (3) | Whenever Seam instantiates a component, it binds the new instance to a context variable in the component's default context. The default context is specified using the @Scope annotation. The User bean is a session scoped component. |
| (4) | The EJB standard @Table annotation indicates that the User class is mapped to the users table. |
| (5) | name, password and username are the persistent attributes of the entity bean. All of our persistent attributes define accessor methods. These are needed when this component is used by JSF in the render response and update model values phases. |
| (6) | An empty constructor is both required by both the EJB specification and by Seam. |
| (7) | The @NotNull and @Length annotations are part of the Hibernate Validator framework. Seam integrates Hibernate Validator and lets you use it for data validation (even if you are not using Hibernate for persistence). |
| (8) | The EJB standard @Id annotation indicates the primary key attribute of the entity bean. |
The most important things to notice in this example are the @Name and @Scope annotations. These annotations establish that this class is a Seam component.
We'll see below that the properties of our User class are bound to directly to JSF components and are populated by JSF during the update model values phase. We don't need any tedious glue code to copy data back and forth between the JSP pages and the entity bean domain model.
However, entity beans shouldn't do transaction management or database access. So we can't use this component as a JSF action listener. For that we need a session bean.
Most Seam application use session beans as JSF action listeners (you can use JavaBeans instead if you like).
We have exactly one JSF action in our application, and one session bean method attached to it. In this case, we'll use a stateless session bean, since all the state associated with our action is held by the User bean.
This is the only really interesting code in the example!
Example 1.2.
@Stateless (1) @Name("register") public class RegisterAction implements Register { @In (2) private User user; @PersistenceContext (3) private EntityManager em; @Logger (4) private Log log; public String register() (5) { List existing = em.createQuery("select username from User where username=:username") .setParameter("username", user.getUsername()) .getResultList(); if (existing.size()==0) { em.persist(user); log.info("Registered new user #{user.username}"); (6) return "/registered.jsp"; (7) } else { FacesMessages.instance().add("User #{user.username} already exists"); (8) return null; } } }
| (1) | The EJB standard @Stateless annotation marks this class as stateless session bean. |
| (2) | The @In annotation marks an attribute of the bean as injected by Seam. In this case, the attribute is injected from a context variable named user (the instance variable name). |
| (3) | The EJB standard @PersistenceContext annotation is used to inject the EJB3 entity manager. |
| (4) | The Seam @Logger annotation is used to inject the component's Log instance. |
| (5) | The action listener method uses the standard EJB3 EntityManager API to interact with the database, and returns the JSF outcome. Note that, since this is a sesson bean, a transaction is automatically begun when the register() method is called, and committed when it completes. |
| (6) | The Log API lets us easily display templated log messages. |
| (7) | JSF action listener methods return a string-valued outcome that determines what page will be displayed next. A null outcome (or a void action listener method) redisplays the previous page. In plain JSF, it is normal to always use a JSF navigation rule to determine the JSF view id from the outcome. For complex application this indirection is useful and a good practice. However, for very simple examples like this one, Seam lets you use the JSF view id as the outcome, eliminating the requirement for a navigation rule. Note that when you use a view id as an outcome, Seam always performs a browser redirect. |
| (8) | Seam provides a number of built-in components to help solve common problems. The FacesMessages component makes it easy to display templated error or success messages. Built-in Seam components may be obtained by injection, or by calling an instance() method. |
Note that we did not explicitly specify a @Scope this time. Each Seam component type has a default scope if not explicitly specified. For stateless session beans, the default scope is the stateless context. Actually, all stateless session beans belong in the stateless context.
Our session bean action listener performs the business and persistence logic for our mini-application. In more complex applications, we might need to layer the code and refactor persistence logic into a dedicated data access component. That's perfectly trivial to do. But notice that Seam does not force you into any particular strategy for application layering.
Furthermore, notice that our session bean has simultaneous access to context associated with the web request (the form values in the User object, for example), and state held in transactional resources (the EntityManager object). This is a break from traditional J2EE architectures. Again, if you are more comfortable with the traditional J2EE layering, you can certainly implement that in a Seam application. But for many applications, it's simply not very useful.
Naturally, our session bean needs a local interface.
That's the end of the Java code. Now onto the deployment descriptors.
If you've used many Java frameworks before, you'll be used to having to declate all your component classes in some kind of XML file that gradually grows more and more unmanageable as your project matures. You'll be relieved to know that Seam does not require that application components be accompanied by XML. Most Seam applications require a very small amount of XML that does not grow very much as the project gets bigger.
Nevertheless, it is often useful to be able to provide for some external configuration of some components (particularly the components built in to Seam). You have a couple of options here, but the most flexible option is to provide this configuration in a file called components.xml, located in the WEB-INF directory. We'll use the components.xml file to tell Seam how to find our EJB components in JNDI:
Example 1.4.
<components>
<component name="org.jboss.seam.core.init">
<!-- JNDI name pattern for JBoss EJB 3.0 -->
<property name="jndiPattern">#{ejbName}/local</property>
</component>
</components>This code configures a property named jndiPattern of a built-in Seam component named org.jboss.seam.core.init.
The presentation layer for our mini-application will be deployed in a WAR. So we'll need a web deployment descriptor.
Example 1.5.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="2.4"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd">
<!-- Seam -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.jboss.seam.servlet.SeamListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- MyFaces -->
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.apache.myfaces.webapp.StartupServletContextListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>javax.faces.STATE_SAVING_METHOD</param-name>
<param-value>client</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>javax.faces.webapp.FacesServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<!-- Faces Servlet Mapping -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.seam</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>This web.xml file configures Seam and MyFaces. The configuration you see here is pretty much identical in all Seam applications.
All Seam applications use JSF views as the presentation layer. So we'll need faces-config.xml.
Example 1.6.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE faces-config
PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD JavaServer Faces Config 1.0//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-facesconfig_1_0.dtd">
<faces-config>
<!-- A phase listener is needed by all Seam applications -->
<lifecycle>
<phase-listener>org.jboss.seam.jsf.SeamPhaseListener</phase-listener>
</lifecycle>
</faces-config>The faces-config.xml file integrates Seam into JSF. Note that we don't need any JSF managed bean declarations! The managed beans are the Seam components. In Seam applications, the faces-config.xml is used much less often than in plain JSF.
In fact, once you have all the basic descriptors set up, the only XML you need to write as you add new functionality to a Seam application is the navigation rules, and possibly jBPM process definitions. Seam takes the view that process flow and configuration data are the only things that truly belong in XML.
In this simple example, we don't even need a navigation rule, since we decided to embed the view id in our action code.
The ejb-jar.xml file integrates Seam with EJB3, by attaching the SeamInterceptor to all session beans in the archive.
<ejb-jar>
<assembly-descriptor>
<interceptor-binding>
<ejb-name>*</ejb-name>
<interceptor-class>org.jboss.seam.ejb.SeamInterceptor</interceptor-class>
</interceptor-binding>
</assembly-descriptor>
</ejb-jar>The persistence.xml file tells the EJB persistence provider where to find the datasource, and contains some vendor-specific settings. In this case, enables automatic schema export at startup time.
<persistence>
<persistence-unit name="userDatabase">
<provider>org.hibernate.ejb.HibernatePersistence</provider>
<jta-data-source>java:/DefaultDS</jta-data-source>
<properties>
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="create-drop"/>
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>The view pages for a Seam application could be implemented using any technology that supports JSF. In this example we use JSP, since it is familiar to most developers and since we have minimal requirements here anyway. (But if you take our advice, you'll use Facelets for your own applications.)
Example 1.7.
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" prefix="h" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" prefix="f" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://jboss.com/products/seam/taglib" prefix="s" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Register New User</title>
</head>
<body>
<f:view>
<h:form>
<table border="0">
<s:validateAll>
<tr>
<td>Username</td>
<td><h:inputText value="#{user.username}"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Real Name</td>
<td><h:inputText value="#{user.name}"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Password</td>
<td><h:inputSecret value="#{user.password}"/></td>
</tr>
</s:validateAll>
</table>
<h:messages/>
<h:commandButton type="submit" value="Register" action="#{register.register}"/>
</h:form>
</f:view>
</body>
</html>The only thing here that is specific to Seam is the <s:validateAll> tag. This JSF component tells JSF to validate all the contained input fields against the Hibernate Validator annotations specified on the entity bean.
Example 1.8.
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" prefix="h" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" prefix="f" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Successfully Registered New User</title>
</head>
<body>
<f:view>
Welcome, <h:outputText value="#{user.name}"/>,
you are successfully registered as <h:outputText value="#{user.username}"/>.
</f:view>
</body>
</html>This is a boring old JSP pages using standard JSF components. There is nothing specific to Seam here.
Finally, since our application is deployed as an EAR, we need a deployment descriptor there, too.
Example 1.9.
<application>
<display-name>Seam</display-name>
<module>
<web>
<web-uri>jboss-seam-registration.war</web-uri>
<context-root>/seam-registration</context-root>
</web>
</module>
<module>
<ejb>jboss-seam-registration.jar</ejb>
</module>
<module>
<java>jboss-seam.jar</java>
</module>
</application>This deployment descriptor links modules in the enterprise archive and binds the web application to the context root /seam-registration.
We've now seen all the files in the entire application!
When the form is submitted, JSF asks Seam to resolve the variable named user. Since there is no value already bound to that name (in any Seam context), Seam instantiates the user component, and returns the resulting User entity bean instance to JSF after storing it in the Seam session context.
The form input values are now validated against the Hibernate Validator constraints specified on the User entity. If the constraints are violated, JSF redisplays the page. Otherwise, JSF binds the form input values to properties of the User entity bean.
Next, JSF asks Seam to resolve the variable named register. Seam finds the RegisterAction stateless session bean in the stateless context and returns it. JSF invokes the register() action listener method.
Seam intercepts the method call and injects the User entity from the Seam session context, before continuing the invocation.
The register() method checks if a user with the entered username already exists. If so, an error message is queued with the FacesMessages component, and a null outcome is returned, causing a page redisplay. The FacesMessages component interpolates the JSF expression embedded in the message string and adds a JSF FacesMessage to the view.
If no user with that username exists, the "/registered.jsp" outcome triggers a browser redirect to the registered.jsp page. When JSF comes to render the page, it asks Seam to resolve the variable named user and uses property values of the returned User entity from Seam's session scope.
Clickable lists of database search results are such an important part of any online application that Seam provides special functionality on top of JSF to make it easier to query data using EJB-QL or HQL and display it as a clickable list using a JSF <h:dataTable>. The messages example demonstrates this functionality.
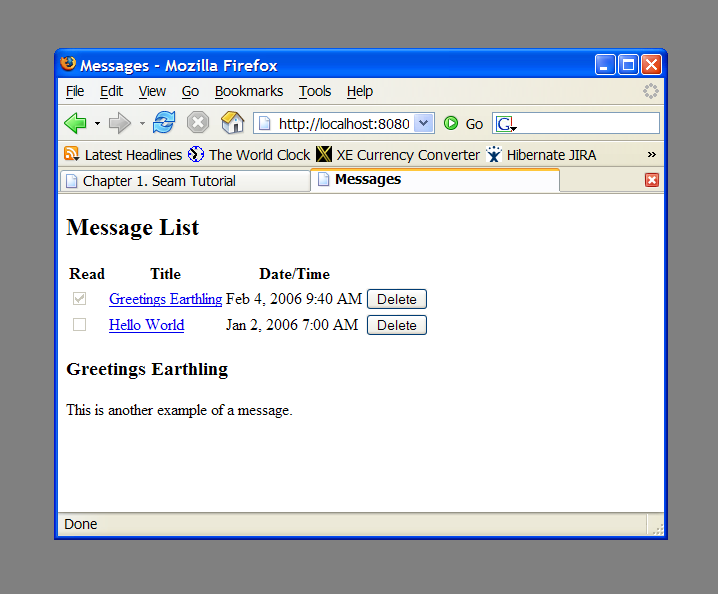
The message list example has one entity bean, Message, one session bean, MessageListBean and one JSP.
The Message entity defines the title, text, date and time of a message, and a flag indicating whether the message has been read:
Example 1.10.
@Entity
@Name("message")
@Scope(EVENT)
public class Message implements Serializable
{
private Long id;
private String title;
private String text;
private boolean read;
private Date datetime;
@Id @GeneratedValue
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
@NotNull @Length(max=100)
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
@NotNull @Lob
public String getText() {
return text;
}
public void setText(String text) {
this.text = text;
}
@NotNull
public boolean isRead() {
return read;
}
public void setRead(boolean read) {
this.read = read;
}
@NotNull
@Basic @Temporal(TemporalType.TIMESTAMP)
public Date getDatetime() {
return datetime;
}
public void setDatetime(Date datetime) {
this.datetime = datetime;
}
}Just like in the previous example, we have a session bean, MessageManagerBean, which defines the action listener methods for the two buttons on our form. One of the buttons selects a message from the list, and displays that message. The other button deletes a message. So far, this is not so different to the previous example.
But MessageManagerBean is also responsible for fetching the list of messages the first time we navigate to the message list page. There are various ways the user could navigate to the page, and not all of them are preceded by a JSF action—the user might have bookmarked the page, for example. So the job of fetching the message list takes place in a Seam factory method, instead of in an action listener method.
We want to cache the list of messages in memory between server requests, so we will make this a stateful session bean.
Example 1.11.
@Stateful
@Scope(SESSION)
@Name("messageManager")
public class MessageManagerBean implements Serializable, MessageManager
{
@DataModel (1)
private List<Message> messageList;
@DataModelSelection (2)
@Out(required=false) (3)
private Message message;
@PersistenceContext(type=EXTENDED) (4)
private EntityManager em;
@Factory("messageList") (5)
public void findMessages()
{
messageList = em.createQuery("from Message msg order by msg.datetime desc").getResultList();
}
public void select() (6)
{
message.setRead(true);
}
public void delete() (7)
{
messageList.remove(message);
em.remove(message);
message=null;
}
@Remove @Destory (8)
public void destroy() {}
}| (1) | The @DataModel annotation exposes an attibute of type java.util.List to the JSF page as an instance of javax.faces.model.DataModel. This allows us to use the list in a JSF <h:dataTable> with clickable links for each row. In this case, the DataModel is made available in a session context variable named messageList. |
| (2) | The @DataModelSelection annotation tells Seam to inject the List element that corresponded to the clicked link. |
| (3) | The @Out annotation then exposes the selected value directly to the page. So ever time a row of the clickable list is selected, the Message is injected to the attribute of the stateful bean, and the subsequently outjected to the event context variable named message. |
| (4) | This stateful bean has an EJB3 extended persistence context. The messages retrieved in the query remain in the managed state as long as the bean exists, so any subsequent method calls to the stateful bean can update them without needing to make any explicit call to the EntityManager. |
| (5) | The first time we navigate to the JSP page, there will be no value in the messageList context variable. The @Factory annotation tells Seam to create an instance of MessageManagerBean and invoke the findMessages() method to initialize the value. We call findMessages() a factory method for messages. |
| (6) | The select() action listener method marks the selected Message as read, and updates it in the database. |
| (7) | The delete() action listener method removes the selected Message from the database. |
| (8) | All stateful session bean Seam components must have a method marked @Remove @Destroy to ensure that Seam will remove the stateful bean when the Seam context ends, and clean up any server-side state. |
Note that this is a session-scoped Seam component. It is associated with the user login session, and all requests from a login session share the same instance of the component. (In Seam applications, we usually use session-scoped components sparingly.)
All session beans have a business interface, of course.
@Local
public interface MessageManager
{
public void findMessages();
public void select();
public void delete();
public void destroy();
}From now on, we won't show local interfaces in our code examples.
Let's skip over components.xml, persistence.xml, web.xml, ejb-jar.xml, faces-config.xml and application.xml since they are much the same as the previous example, and go straight to the JSP.
The JSP page is a straightforward use of the JSF <h:dataTable> component. Again, nothing specific to Seam.
Example 1.12.
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" prefix="h" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" prefix="f" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Messages</title>
</head>
<body>
<f:view>
<h:form>
<h2>Message List</h2>
<h:outputText value="No messages to display" rendered="#{messageList.rowCount==0}"/>
<h:dataTable var="msg" value="#{messageList}" rendered="#{messageList.rowCount>0}">
<h:column>
<f:facet name="header">
<h:outputText value="Read"/>
</f:facet>
<h:selectBooleanCheckbox value="#{msg.read}" disabled="true"/>
</h:column>
<h:column>
<f:facet name="header">
<h:outputText value="Title"/>
</f:facet>
<h:commandLink value="#{msg.title}" action="#{messageManager.select}"/>
</h:column>
<h:column>
<f:facet name="header">
<h:outputText value="Date/Time"/>
</f:facet>
<h:outputText value="#{msg.datetime}">
<f:convertDateTime type="both" dateStyle="medium" timeStyle="short"/>
</h:outputText>
</h:column>
<h:column>
<h:commandButton value="Delete" action="#{messageManager.delete}"/>
</h:column>
</h:dataTable>
<h3><h:outputText value="#{message.title}"/></h3>
<div><h:outputText value="#{message.text}"/></div>
</h:form>
</f:view>
</body>
</html>The first time we navigate to the messages.jsp page, whether by a JSF postback (faces request) or a direct browser GET request (non-faces request), the page will try to resolve the messageList context variable. Since this context variable is not initialized, Seam will call the factory method findMessages(), which performs a query against the database and results in a DataModel being outjected. This DataModel provides the row data needed for rendering the <h:dataTable>.
When the user clicks the <h:commandLink>, JSF calls the select() action listener. Seam intercepts this call and injects the selected row data into the message attribute of the messageManager component. The action listener fires, marking the selected Message as read. At the end of the call, Seam outjects the selected Message to the context variable named message. Next, the EJB container commits the transaction, and the change to the Message is flushed to the database. Finally, the page is re-rendered, redisplaying the message list, and displaying the selected message below it.
If the user clicks the <h:commandButton>, JSF calls the delete() action listener. Seam intercepts this call and injects the selected row data into the message attribute of the messageList component. The action listener fires, removing the selected Message from the list, and also calling remove() on the EntityManager. At the end of the call, Seam refreshes the messageList context variable and clears the context variable named message. The EJB container commits the transaction, and deletes the Message from the database. Finally, the page is re-rendered, redisplaying the message list.
jBPM provides sophisticated functionality for workflow and task management. To get a small taste of how jBPM integrates with Seam, we'll show you a simple "todo list" application. Since managing lists of tasks is such core functionality for jBPM, there is hardly any Java code at all in this example.
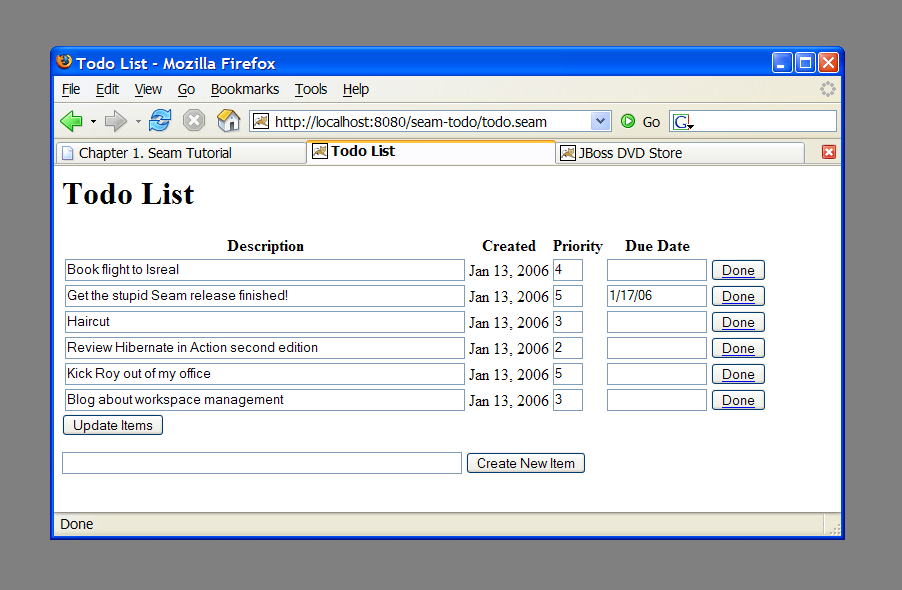
The center of this example is the jBPM process definition. There are also two JSPs and two trivial JavaBeans (There was no reason to use session beans, since they do not access the database, or have any other transactional behavior). Let's start with the process definition:
Example 1.13.
<process-definition name="todo"> <start-state name="start"> (1) <transition to="todo"/> </start-state> <task-node name="todo"> (2) <task name="todo" description="#{todoList.description}"> (3) <assignment actor-id="#{actor.id}"/> (4) </task> <transition to="done"/> </task-node> <end-state name="done"/> (5) </process-definition>
| (1) | The <start-state> node represents the logical start of the process. When the process starts, it immediately transitions to the todo node. |
| (2) | The <task-node> node represents a wait state, where business process execution pauses, waiting for one or more tasks to be performed. |
| (3) | The <task> element defines a task to be performed by a user. Since there is only one task defined on this node, when it is complete, execution resumes, and we transition to the end state. The task gets its description from a Seam component named todoList (one of the JavaBeans). |
| (4) | Tasks need to be assigned to a user or group of users when they are created. In this case, the task is assigned to the current user, which we get from a built-in Seam component named actor. Any Seam component may be used to perform task assignment. |
| (5) | The <end-state> node defines the logical end of the business process. When execution reaches this node, the process instance is destroyed. |
If we view this process definition using the process definition editor provided by JBossIDE, this is what it looks like:
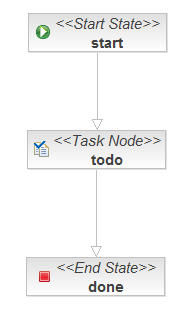
This document defines our business process as a graph of nodes. This is the most trivial possible business process: there is one task to be performed, and when that task is complete, the business process ends.
The first JavaBean handles the login screen login.jsp. Its job is just to initialize the jBPM actor id using the actor component. (In a real application, it would also need to authenticate the user.)
Example 1.14.
@Name("login")
public class Login {
@In(create=true)
private Actor actor;
private String user;
public String getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public String login()
{
actor.setId(user);
return "/todo.jsp";
}
}Here we see the use of @In(create=true), which tells Seam to create an instance of a component, in this case the component named actor, if none currently exists in the context.
The JSP itself is trivial:
Example 1.15.
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" prefix="h"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" prefix="f"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Login</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Login</h1>
<f:view>
<h:form>
<div>
<h:inputText value="#{login.user}"/>
<h:commandButton value="Login" action="#{login.login}"/>
</div>
</h:form>
</f:view>
</body>
</html>The second JavaBean is responsible for starting business process instances, and ending tasks.
Example 1.16.
@Name("todoList")
public class TodoList {
private String description;
public String getDescription() (1)
{
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
@CreateProcess(definition="todo") (2)
public void createTodo() {}
@StartTask @EndTask (3)
public void done() {}
}| (1) | The description property accepts user input form the JSP page, and exposes it to the process definition, allowing the task description to be set. |
| (2) | The Seam @CreateProcess annotation creates a new jBPM process instance for the named process definition. |
| (3) | The Seam @StartTask annotation starts work on a task. The @EndTask ends the task, and allows the business process execution to resume. |
In a more realistic example, @StartTask and @EndTask would not appear on the same method, because there is usually work to be done using the application in order to complete the task.
Finally, the meat of the application is in todo.jsp:
Example 1.17.
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" prefix="h" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" prefix="f" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://jboss.com/products/seam/taglib" prefix="s" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Todo List</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Todo List</h1>
<f:view>
<h:form id="list">
<div>
<h:outputText value="There are no todo items." rendered="#{empty taskInstanceList}"/>
<h:dataTable value="#{taskInstanceList}" var="task" rendered="#{not empty taskInstanceList}">
<h:column>
<f:facet name="header">
<h:outputText value="Description"/>
</f:facet>
<h:inputText value="#{task.description}"/>
</h:column>
<h:column>
<f:facet name="header">
<h:outputText value="Created"/>
</f:facet>
<h:outputText value="#{task.taskMgmtInstance.processInstance.start}">
<f:convertDateTime type="date"/>
</h:outputText>
</h:column>
<h:column>
<f:facet name="header">
<h:outputText value="Priority"/>
</f:facet>
<h:inputText value="#{task.priority}" style="width: 30"/>
</h:column>
<h:column>
<f:facet name="header">
<h:outputText value="Due Date"/>
</f:facet>
<h:inputText value="#{task.dueDate}" style="width: 100">
<f:convertDateTime type="date" dateStyle="short"/>
</h:inputText>
</h:column>
<h:column>
<s:link value="Done" action="#{todoList.done}" taskInstance="#{task}" linkStyle="button"/>
</h:column>
</h:dataTable>
</div>
<div>
<h:messages/>
</div>
<div>
<h:commandButton value="Update Items" action="update"/>
</div>
</h:form>
<h:form id="new">
<div>
<h:inputText value="#{todoList.description}"/>
<h:commandButton value="Create New Item" action="#{todoList.createTodo}"/>
</div>
</h:form>
</f:view>
</body>
</html>Let's take this one piece at a time.
The page renders a list of tasks, which it gets from a built-in Seam component named taskInstanceList. The list is defined inside a JSF form.
<h:form id="list">
<div>
<h:outputText value="There are no todo items." rendered="#{empty taskInstanceList}"/>
<h:dataTable value="#{taskInstanceList}" var="task" rendered="#{not empty taskInstanceList}">
...
</h:dataTable>
</div>
</h:form>Each element of the list is an instance of the jBPM class TaskInstance. The following code simply displays the interesting properties of each task in the list. For the description, priority and due date, we use input controls, to allow the user to update these values.
<h:column>
<f:facet name="header">
<h:outputText value="Description"/>
</f:facet>
<h:inputText value="#{task.description}"/>
</h:column>
<h:column>
<f:facet name="header">
<h:outputText value="Created"/>
</f:facet>
<h:outputText value="#{task.taskMgmtInstance.processInstance.start}">
<f:convertDateTime type="date"/>
</h:outputText>
</h:column>
<h:column>
<f:facet name="header">
<h:outputText value="Priority"/>
</f:facet>
<h:inputText value="#{task.priority}" style="width: 30"/>
</h:column>
<h:column>
<f:facet name="header">
<h:outputText value="Due Date"/>
</f:facet>
<h:inputText value="#{task.dueDate}" style="width: 100">
<f:convertDateTime type="date" dateStyle="short"/>
</h:inputText>
</h:column>This button ends the task by calling the action method annotated @StartTask @EndTask. It passes the task id to Seam as a request parameter:
<h:column>
<s:link value="Done" action="#{todoList.done}" taskInstance="#{task}" linkStyle="button"/>
</h:column>(Note that this is using a Seam <s:link> JSF control from the seam-ui.jar package.)
This button is used to update the properties of the tasks. When the form is submitted, Seam and jBPM will make any changes to the tasks persistent. There is no need for any action listener method:
<h:commandButton value="Update Items" action="update"/>
A second form on the page is used to create new items, by calling the action method annotated @CreateProcess.
<h:form id="new">
<div>
<h:inputText value="#{todoList.description}"/>
<h:commandButton value="Create New Item" action="#{todoList.createTodo}"/>
</div>
</h:form>There are several other files needed for the example, but they are just standard jBPM and Seam configuration and not very interesting.
For Seam applications with relatively freeform (ad hoc) navigation, JSF navigation rules are a perfectly good way to define the page flow. For applications with a more constrained style of navigation, especially for user interfaces which are more stateful, navigation rules make it difficult to really understand the flow of the system. To understand the flow, you need to piece it together from the view pages, the actions and the navigation rules.
Seam allows you to use a jPDL process definition to define pageflow. The simple number guessing example shows how this is done.
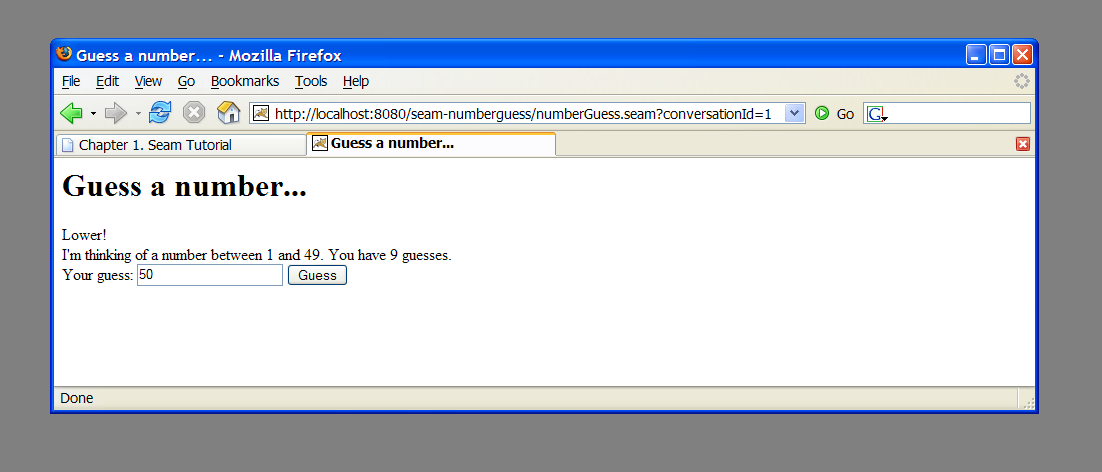
The example is implemented using one JavaBean, three JSP pages and a jPDL pageflow definition. Let's begin with the pageflow:
Example 1.18.
<pageflow-definition name="numberGuess">
<start-page name="displayGuess" view-id="/numberGuess.jsp">
<redirect/>
<transition name="guess" to="evaluateGuess">
<action expression="#{numberGuess.guess}" />
</transition> (1)
</start-page> (2)
(3)
<decision name="evaluateGuess" expression="#{numberGuess.correctGuess}">
<transition name="true" to="win"/>
<transition name="false" to="evaluateRemainingGuesses"/>
</decision> (4)
<decision name="evaluateRemainingGuesses" expression="#{numberGuess.lastGuess}">
<transition name="true" to="lose"/>
<transition name="false" to="displayGuess"/>
</decision>
<page name="win" view-id="/win.jsp">
<redirect/>
<end-conversation />
</page>
<page name="lose" view-id="/lose.jsp">
<redirect/>
<end-conversation />
</page>
</pageflow-definition>| (1) | The <page> element defines a wait state where the system displays a particular JSF view and waits for user input. The view-id is the same JSF view id used in plain JSF navigation rules. The redirect attribute tells Seam to use post-then-redirect when navigating to the page. (This results in friendly browser URLs.) |
| (2) | The <transition> element names a JSF outcome. The transition is triggered when a JSF action results in that outcome. Execution will then proceed to the next node of the pageflow graph, after invocation of any jBPM transition actions. |
| (3) | A transition <action> is just like a JSF action, except that it occurs when a jBPM transition occurs. The transition action can invoke any Seam component. |
| (4) | A <decision> node branches the pageflow, and determines the next node to execute by evaluating a JSF EL expression. |
Here is what the pageflow looks like in the JBossIDE pageflow editor:
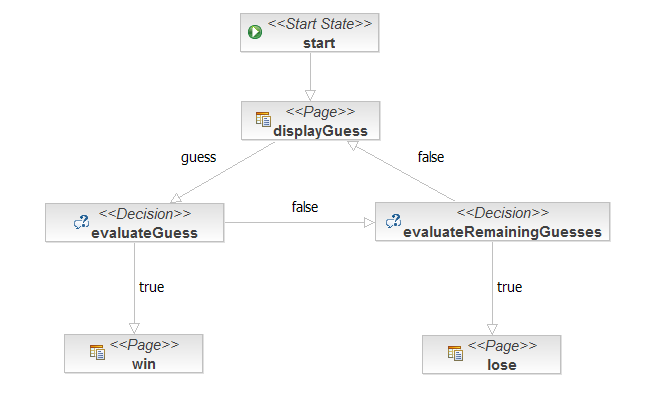
Now that we have seen the pageflow, it is very, very easy to understand the rest of the application!
Here is the main page of the application, numberGuess.jsp:
Example 1.19.
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" prefix="h"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" prefix="f"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Guess a number...</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Guess a number...</h1>
<f:view>
<h:form>
<h:outputText value="Higher!" rendered="#{numberGuess.randomNumber>numberGuess.currentGuess}" />
<h:outputText value="Lower!" rendered="#{numberGuess.randomNumber<numberGuess.currentGuess}" />
<br />
I'm thinking of a number between <h:outputText value="#{numberGuess.smallest}" /> and
<h:outputText value="#{numberGuess.biggest}" />. You have
<h:outputText value="#{numberGuess.remainingGuesses}" /> guesses.
<br />
Your guess:
<h:inputText value="#{numberGuess.currentGuess}" id="guess" required="true">
<f:validateLongRange
maximum="#{numberGuess.biggest}"
minimum="#{numberGuess.smallest}"/>
</h:inputText>
<h:commandButton type="submit" value="Guess" action="guess" />
<br/>
<h:message for="guess" style="color: red"/>
</h:form>
</f:view>
</body>
</html>Notice how the command button names the guess transition instead of calling an action directly.
The win.jsp page is predictable:
Example 1.20.
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" prefix="h"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" prefix="f"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>You won!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>You won!</h1>
<f:view>
Yes, the answer was <h:outputText value="#{numberGuess.currentGuess}" />.
It took you <h:outputText value="#{numberGuess.guessCount}" /> guesses.
Would you like to <a href="numberGuess.seam">play again</a>?
</f:view>
</body>
</html>As is lose.jsp (which I can't be bothered copy/pasting). Finally, the JavaBean Seam component:
Example 1.21.
@Name("numberGuess")
@Scope(ScopeType.CONVERSATION)
public class NumberGuess {
private int randomNumber;
private Integer currentGuess;
private int biggest;
private int smallest;
private int guessCount;
private int maxGuesses;
@Create (1)
@Begin(pageflow="numberGuess") (2)
public void begin()
{
randomNumber = new Random().nextInt(100);
guessCount = 0;
biggest = 100;
smallest = 1;
}
public void setCurrentGuess(Integer guess)
{
this.currentGuess = guess;
}
public Integer getCurrentGuess()
{
return currentGuess;
}
public void guess()
{
if (currentGuess>randomNumber)
{
biggest = currentGuess - 1;
}
if (currentGuess<randomNumber)
{
smallest = currentGuess + 1;
}
guessCount ++;
}
public boolean isCorrectGuess()
{
return currentGuess==randomNumber;
}
public int getBiggest()
{
return biggest;
}
public int getSmallest()
{
return smallest;
}
public int getGuessCount()
{
return guessCount;
}
public boolean isLastGuess()
{
return guessCount==maxGuesses;
}
public int getRemainingGuesses() {
return maxGuesses-guessCount;
}
public void setMaxGuesses(int maxGuesses) {
this.maxGuesses = maxGuesses;
}
public int getMaxGuesses() {
return maxGuesses;
}
public int getRandomNumber() {
return randomNumber;
}
}| (1) | The first time a JSP page asks for a numberGuess component, Seam will create a new one for it, and the @Create method will be invoked, allowing the component to initialize itself. |
| (2) | The @Begin annotation starts a Seam conversation (much more about that later), and specifies the pageflow definition to use for the conversation's page flow. |
As you can see, this Seam component is pure business logic! It doesn't need to know anything at all about the user interaction flow. This makes the component potentially more reuseable.
The booking application is a complete hotel room reservation system incorporating the following features:
User registration
Login
Logout
Set password
Hotel search
Hotel selection
Room reservation
Reservation confirmation
Existing reservation list
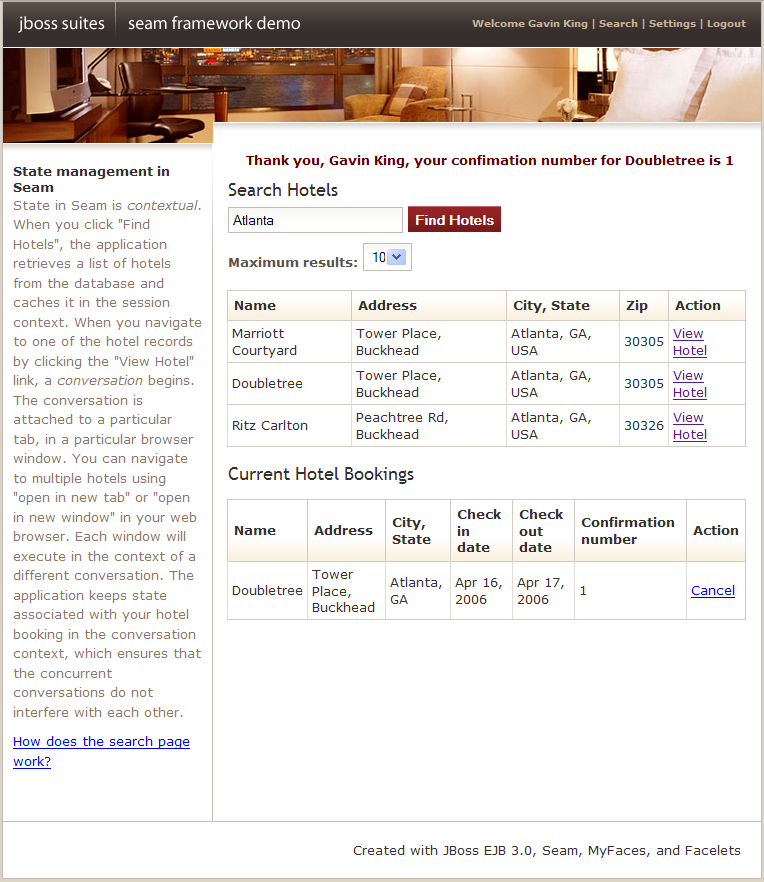
The booking application uses JSF, EJB 3.0 and Seam, together with Facelets for the view. There is also a port of this application to JSF, Facelets, Seam, JavaBeans and Hibernate3.
One of the things you'll notice if you play with this application for long enough is that it is extremely robust. You can play with back buttons and browser refresh and opening multiple windows and entering nonsensical data as much as you like and you will find it very difficult to make the application crash. You might think that we spent weeks testing and fixing bugs to achive this. Actually, this is not the case. Seam was designed to make it very straightforward to build robust web applications and a lot of robustness that you are probably used to having to code yourself comes naturally and automatically with Seam.
As you browse the sourcecode of the example application, and learn how the application works, observe how the declarative state management and integrated validation has been used to achieve this robustness.
The project structure is identical to the previous one, to install and deploy this application, please refer to Section 1.1, “Try the examples”. Once you've successfully started the application, you can access it by pointing your browser to http://localhost:8080/seam-booking/
Just ten classes (plus six session beans local interfaces and 1 annotation interface) where used to implement this application. Six session bean action listeners contain all the business logic for the listed features.
- BookingListAction retrieves existing bookings for the currently logged in user.
- ChangePasswordAction updates the password of the currently logged in user.
- HotelBookingAction implements the core functionality of the application: hotel room searching, selection, booking and booking confirmation. This functionality is implemented as a conversation, so this is the most interesting class in the application.
- LoginAction validates the login details and retrieves the logged in user.
- LogoutAction ends the login session.
- RegisterAction registers a new system user.
Three entity beans implement the application's persistent domain model.
- Hotel is an entity bean that represent a hotel
- Booking is an entity bean that represents an existing booking
- User is an entity bean to represents a user who can make hotel bookings
Finally, the LoggedIn annotation and the LoggedInInterceptor are used to protect actions that require a logged in user.
We encourage you browse the sourcecode at your pleasure. In this tutorial we'll concentrate upon one particular piece of functionality: hotel search, selection, booking and confirmation. From the point of view of the user, everything from selecting a hotel to confirming a booking is one continuous unit of work, a conversation. Searching, however, is not part of the conversation. The user can select multiple hotels from the same search results page, in different browser tabs.
Most web application architectures have no first class construct to represent a conversation. This causes enormous problems managing state associated with the conversation. Usually, Java web applications use a combination of two techniques: first, some state is thrown into the HttpSession; second, persistable state is flushed to the database after every request, and reconstructed from the database at the beginning of each new request.
Since the database is the least scalable tier, this often results in an utterly unacceptable lack of scalability. Added latency is also a problem, due to the extra traffic to and from the database on every request. To reduce this redundant traffic, Java applications often introduce a data (second-level) cache that keeps commonly accessed data between requests. This cache is necessarily inefficient, because invalidation is based upon an LRU policy instead of being based upon when the user has finished working with the data. Furthermore, because the cache is shared between many concurrent transactions, we've introduced a whole raft of problem's associated with keeping the cached state consistent with the database.
Now consider the state held in the HttpSession. By very careful programming, we might be able to control the size of the session data. This is a lot more difficult than it sounds, since web browsers permit ad hoc non-linear navigation. But suppose we suddenly discover a system requirement that says that a user is allowed to have mutiple concurrent conversations, halfway through the development of the system (this has happened to me). Developing mechanisms to isolate session state associated with different concurrent conversations, and incorporating failsafes to ensure that conversation state is destroyed when the user aborts one of the conversations by closing a browser window or tab is not for the faint hearted (I've implemented this stuff twice so far, once for a client application, once for Seam, but I'm famously psychotic).
Now there is a better way.
Seam introduces the conversation context as a first class construct. You can safely keep conversational state in this context, and be assured that it will have a well-defined lifecycle. Even better, you won't need to be continually pushing data back and forth between the application server and the database, since the conversation context is a natural cache of data that the user is currently working with.
Usually, the components we keep in the conversation context are stateful session beans. (We can also keep entity beans and JavaBeans in the conversation context.) There is an ancient canard in the Java community that stateful session beans are a scalability killer. This may have been true in 1998 when WebFoobar 1.0 was released. It is no longer true today. Application servers like JBoss 4.0 have extremely sophisticated mechanisms for stateful session bean state replication. (For example, the JBoss EJB3 container performs fine-grained replication, replicating only those bean attribute values which actually changed.) Note that all the traditional technical arguments for why stateful beans are inefficient apply equally to the HttpSession, so the practice of shifting state from business tier stateful session bean components to the web session to try and improve performance is unbelievably misguided. It is certainly possible to write unscalable applications using stateful session beans, by using stateful beans incorrectly, or by using them for the wrong thing. But that doesn't mean you should never use them. Anyway, Seam guides you toward a safe usage model. Welcome to 2005.
OK, I'll stop ranting now, and get back to the tutorial.
The booking example application shows how stateful components with different scopes can collaborate together to achieve complex behaviors. The main page of the booking application allows the user to search for hotels. The search results are kept in the Seam session scope. When the user navigates to one of these hotels, a conversation begins, and a conversation scoped component calls back to the session scoped component to retrieve the selected hotel.
The search functionality is implemented using a session-scope stateful session bean, similar to the one we saw in the message list example above.
Example 1.22.
@Stateful (1) @Name("hotelSearch") @Scope(ScopeType.SESSION) @LoggedIn (2) public class HotelSearchingAction implements HotelSearching { @PersistenceContext private EntityManager em; private String searchString; private int pageSize = 10; @DataModel (3) private List<Hotel> hotels; @DataModelSelection (4) private Hotel selectedHotel; public String find() { String searchPattern = searchString==null ? "%" : '%' + searchString.toLowerCase().replace('*', '%') + '%'; hotels = em.createQuery("from Hotel where lower(name) like :search or lower(city) like :search or lower(zip) like :search or lower(address) like :search") .setParameter("search", searchPattern) .setMaxResults(pageSize) .getResultList(); return "main"; } public Hotel getSelectedHotel() { return selectedHotel; } public int getPageSize() { return pageSize; } public void setPageSize(int pageSize) { this.pageSize = pageSize; } public String getSearchString() { return searchString; } public void setSearchString(String searchString) { this.searchString = searchString; } @Destroy @Remove (5) public void destroy() {} }
| (1) | The EJB standard @Stateful annotation identifies this class as a stateful session bean. Stateful session beans are scoped to the conversation context by default. |
| (2) | The @LoggedIn annotation applies a custom Seam interceptor to the component. This works because @LoggedIn is marked with an @Interceptor meta-annotation. |
| (3) | The @DataModel annotation exposes a List as a JSF ListDataModel. This makes it easy to implement clickable lists for search screens. In this case, the list of hotels is exposed to the page as a ListDataModel in the conversation variable named hotels. |
| (4) | The @DataModelSelection annotation defines a field or setter as holding the selected row for the corresponding @DataModel property. |
| (5) | The EJB standard @Remove annotation specifies that a stateful session bean should be removed and its state destroyed after invocation of the annotated method. In Seam, all stateful session beans should define a method marked @Destroy @Remove. This is the EJB remove method that will be called when Seam destroys the session context. Actually, the @Destroy annotation is of more general usefulness, since it can be used for any kind of cleanup that should happen when any Seam context ends. If you don't have an @Destroy @Remove method, state will leak and you will suffer performance problems. |
Now lets see how the booking example application uses a conversation-scoped stateful session bean to achieve a natural cache of persistent data related to the conversation. The following code example is pretty long. But if you think of it as a list of scripted actions that implement the various steps of the conversation, it's understandable. Read the class from top to bottom, as if it were a story.
Example 1.23.
@Stateful
@Name("hotelBooking")
@Conversational(ifNotBegunOutcome="main") (1)
@LoggedIn
public class HotelBookingAction implements HotelBooking
{
@PersistenceContext(type=EXTENDED) (2)
private EntityManager em;
@In(required=false) @Out (3)
private Hotel hotel;
@In(required=false)
@Out(required=false)
@Valid
private Booking booking;
@In
private User user;
@In(create=true)
private transient FacesMessages facesMessages;
@In(required=false)
private BookingList bookingList;
@In
private HotelSearching hotelSearch;
@Begin (4)
public String selectHotel()
{
hotel = em.merge( hotelSearch.getSelectedHotel() );
//hotel = em.find(Hotel.class, hotelId);
return "hotel";
}
public String bookHotel()
{
booking = new Booking(hotel, user);
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
booking.setCheckinDate( calendar.getTime() );
calendar.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 1);
booking.setCheckoutDate( calendar.getTime() );
return "book";
}
public String setBookingDetails()
{
if (booking==null || hotel==null) return "main";
if ( !booking.getCheckinDate().before( booking.getCheckoutDate() ) )
{
facesMessages.add("Check out date must be later than check in date");
return null;
}
else
{
return "confirm";
}
}
@End (5)
public String confirm()
{
if (booking==null || hotel==null) return "main";
em.persist(booking);
if (bookingList!=null) bookingList.refresh();
facesMessages.add("Thank you, #{user.name}, your confimation number for #{hotel.name} is #{booking.id}");
return "confirmed";
}
@End
public String cancel()
{
return "main";
}
@Destroy @Remove (6)
public void destroy() {}
}| (1) | The Seam @Conversational annotation declares this as a conversational component that cannot be invoked outside of a long-running conversation that was started by a call to its @Begin method. If such an invocation does occur, Seam returns the ifNotBegunOutcome to JSF. |
| (2) | This bean uses an EJB3 extended persistence context, so that any entity instances remain managed for the whole lifecycle of the stateful session bean. |
| (3) | The @Out annotation declares that an attribute value is outjected to a context variable after method invocations. In this case, the context variable named hotel will be set to the value of the hotel instance variable after every action listener invocation completes. |
| (4) | The @Begin annotation specifies that the annotated method begins a long-running conversation, so the current conversation context will not be destroyed at the end of the request. Instead, it will be reassociated with every request from the current window, and destroyed either by timeout due to conversation inactivity or invocation of a matching @End method. |
| (5) | The @End annotation specifies that the annotated method ends the current long-running conversation, so the current conversation context will be destroyed at the end of the request. |
| (6) | This EJB remove method will be called when Seam destroys the conversation context. Don't ever forget to define this method! |
HotelBookingAction contains all the action listener methods that implement selection, booking and booking confirmation, and holds state related to this work in its instance variables. We think you'll agree that this code is much cleaner and simpler than getting and setting HttpSession attributes.
Even better, a user can have multiple isolated conversations per login session. Try it! Log in, run a search, and navigate to different hotel pages in multiple browser tabs. You'll be able to work on creating two different hotel reservations at the same time. If you leave any one conversation inactive for long enough, Seam will eventually time out that conversation and destroy its state. If, after ending a conversation, you backbutton to a page of that conversation and try to perform an action, Seam will detect that the conversation was already ended, and redirect you to the search page.
If you check inside the WAR file for the booking application, you'll find seam-ui.jar in the WEB-INF/lib directory. This package contains a number of JSF custom controls that integrate with Seam. The booking application uses the <s:link> control for navigation from the search screen to the hotel page:
<s:link value="View Hotel" action="#{hotelBooking.selectHotel}"/>The use of <s:link> here allows us to attach an action listener to a HTML link without breaking the browser's "open in new window" feature. The standard JSF <h:commandLink> does not work with "open in new window".
The WAR also includes seam-debug.jar. If this jar is deployed in WEB-INF/lib, along with the Facelets, and if you set the following Seam property in web.xml or seam.properties:
<context-param>
<param-name>org.jboss.seam.core.init.debug</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
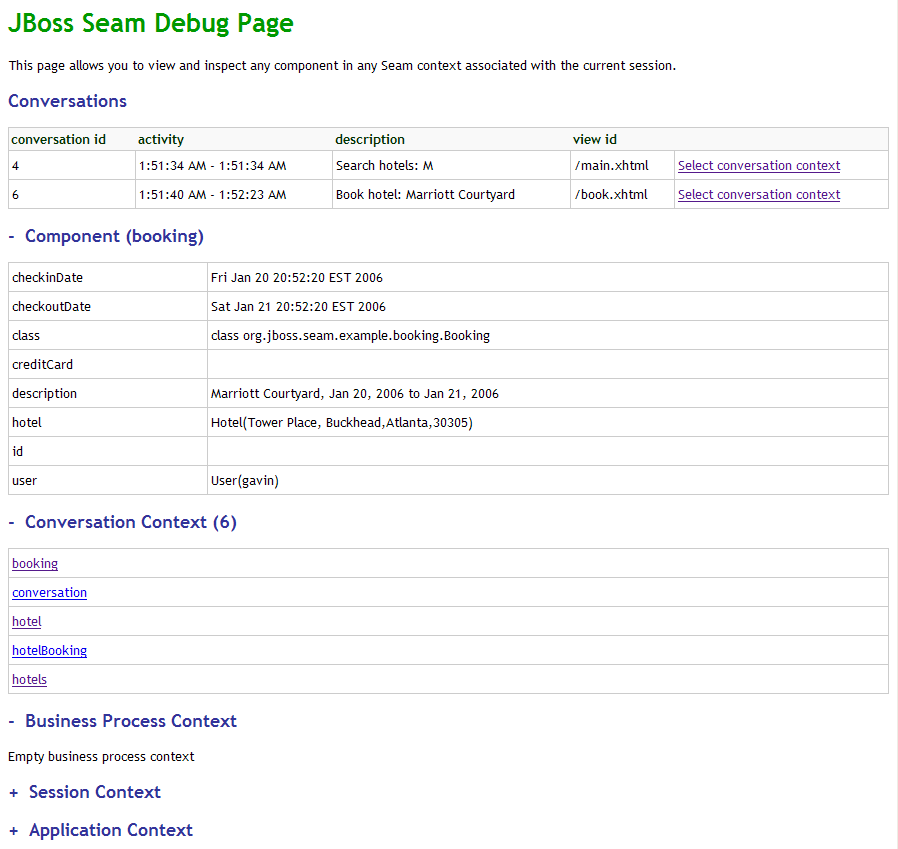
</context-param>Then the Seam debug page will be available. This page lets you browse and inspect the Seam components in any of the Seam contexts associated with your current login session. Just point your browser at http://localhost:8080/seam-booking/debug.seam.
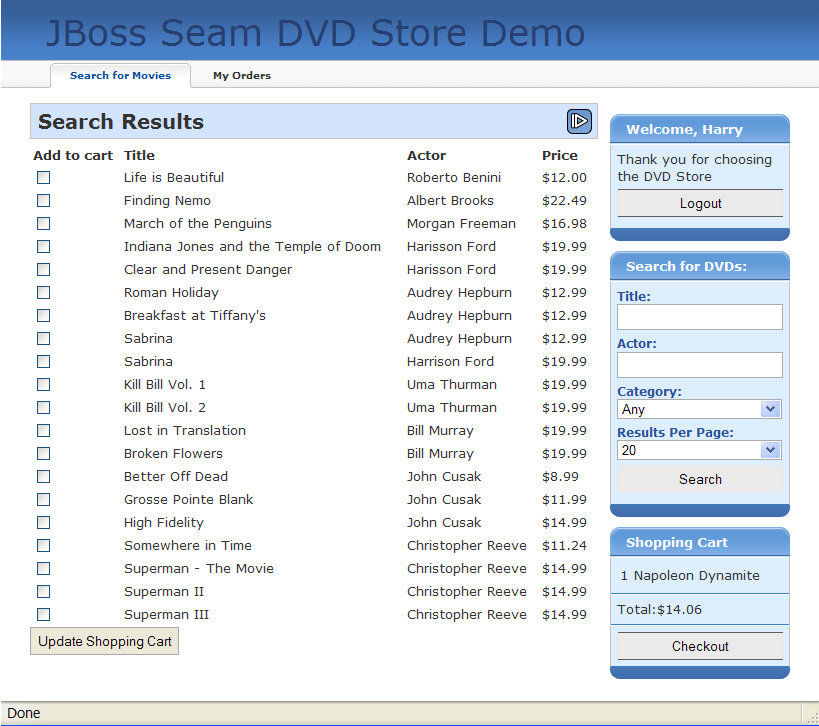
The DVD Store demo application shows the practical usage of jBPM for both task management and pageflow.
The user screens take advantage of a jPDL pageflow to implement searching and shopping cart functionality.
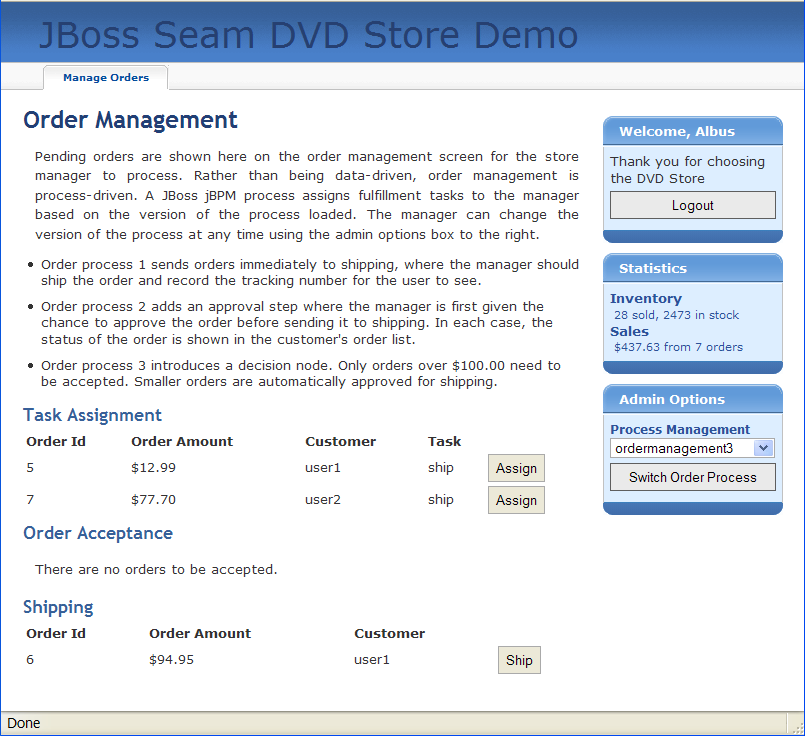
The administration screens take use jBPM to manage the approval and shipping cycle for orders. The business process may even be changed dynamically, by selecting a different process definition!
TODO
Look in the dvdstore directory.
The Issue Tracker demo shows off Seam's workspace management functionality: the conversation switcher, conversation list and breadcrumbs.
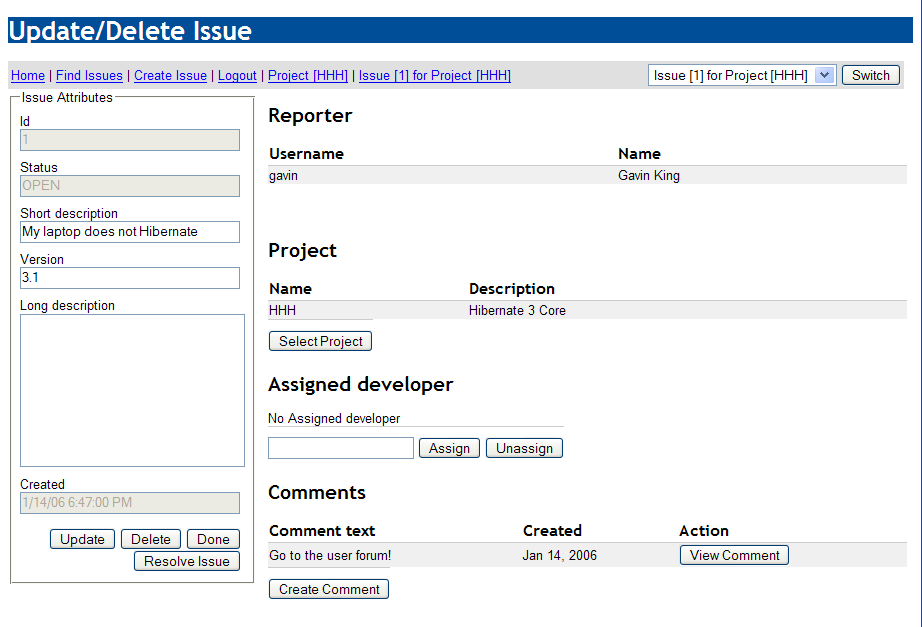
TODO
Look in the issues directory.
The Hibernate Booking demo is a straight port of the Booking demo to an alternative architecture that uses Hibernate for persistence and JavaBeans instead of session beans.
TODO
Look in the hibernate directory.
Seam makes it very easy to implement applications which keep state on the server-side. However, server-side state is not always appropriate, especially in for functionality that serves up content. For this kind of problem we often need to let the user bookmark pages and have a relatively stateless server, so that any page can be accessed at any time, via the bookmark. The Blog example shows how to a implement RESTful application using Seam. Every page of the application can be bookmarked, including the search results page.
The Blog example demonstrates the use of "pull"-style MVC, where instead of using action listener methods to retrieve data and prepare the data for the view, the view pulls data from components as it is being rendered.
This snippet from the index.xhtml facelets page displays a list of recent blog entries:
Example 1.24.
<h:dataTable value="#{blog.recentBlogEntries}" var="blogEntry" rows="3">
<h:column>
<div class="blogEntry">
<h3>#{blogEntry.title}</h3>
<div>
<h:outputText escape="false"
value="#{blogEntry.excerpt==null ? blogEntry.body : blogEntry.excerpt}"/>
</div>
<p>
<h:outputLink value="entry.seam" rendered="#{blogEntry.excerpt!=null}">
<f:param name="blogEntryId" value="#{blogEntry.id}"/>
Read more...
</h:outputLink>
</p>
<p>
[Posted on
<h:outputText value="#{blogEntry.date}">
<f:convertDateTime timeZone="#{blog.timeZone}" locale="#{blog.locale}" type="both"/>
</h:outputText>]
 
<h:outputLink value="entry.seam">[Link]
<f:param name="blogEntryId" value="#{blogEntry.id}"/>
</h:outputLink>
</p>
</div>
</h:column>
</h:dataTable>If we navigate to this page from a bookmark, how does the data used by the <h:dataTable> actually get initialized? Well, what happens is that the Blog is retrieved lazily—"pulled"—when needed, by a Seam component named blog. This is the opposite flow of control that is usual in traditional web action-based frameworks like Struts.
Example 1.25.
@Name("blog")
@Scope(ScopeType.STATELESS)
public class BlogService
{
@In(create=true) (1)
private EntityManager entityManager;
@Unwrap (2)
public Blog getBlog()
{
return (Blog) entityManager.createQuery("from Blog b left join fetch b.blogEntries")
.setHint("org.hibernate.cacheable", true)
.getSingleResult();
}
}| (1) | This component uses a seam-managed persistence context. Unlike the other examples we've seen, this persistence context is managed by Seam, instead of by the EJB3 container. The persistence context spans the entire web request, allowing us to avoid any exceptions that occur when accessing unfetched associations in the view. |
| (2) | The @Unwrap annotation tells Seam to provide the return value of the method—the Blog—instead of the actual BlogService component to clients. This is the Seam manager component pattern. |
This is good so far, but what about bookmarking the result of form submissions, such as a search results page?
The blog example has a tiny form in the top right of each page that allows the user to search for blog entries. This is defined in the facelets template, template.xhtml:
Example 1.26.
<div id="search">
<h:form>
<h:inputText value="#{searchAction.searchPattern}"/>
<h:commandButton value="Search" action="#{searchAction.search}"/>
</h:form>
</div>To implement a bookmarkable search results page, we need to perform a browser redirect after processing the search form submission. Seam provides a built-in component named redirect that makes it very easy to perform redirects with request parameters.
You can either use a templated outcome, with JSF EL expressions as the request parameter values:
Example 1.27.
@Name("searchAction")
public class SearchAction
{
private String searchPattern;
public String getSearchPattern()
{
return searchPattern;
}
public void setSearchPattern(String searchPattern)
{
this.searchPattern = searchPattern;
}
public String search()
{
return "/search.xhtml?searchPattern=#{searchAction.searchPattern}");
}
}Or, if that feels too magical, you can inject and call the redirect component directly:
Example 1.28.
@Name("searchAction")
public class SearchAction
{
@In(create=true)
private Redirect redirect;
private String searchPattern;
public String getSearchPattern()
{
return searchPattern;
}
public void setSearchPattern(String searchPattern)
{
this.searchPattern = searchPattern;
}
public void search()
{
redirect.setViewId("/search.xhtml");
redirect.setParameter("searchPattern", searchPattern);
redirect.execute();
}
}The redirect takes us to the search.xhtml page:
Example 1.29.
<h:dataTable value="#{searchResults}" var="blogEntry">
<h:column>
<div>
<h:outputLink value="entry.seam">
<f:param name="blogEntryId" value="#{blogEntry.id}"/>
#{blogEntry.title}
</h:outputLink>
posted on
<h:outputText value="#{blogEntry.date}">
<f:convertDateTime timeZone="#{blog.timeZone}" locale="#{blog.locale}" type="both"/>
</h:outputText>
</div>
</h:column>
</h:dataTable>Which again uses "pull"-style MVC to retrieve the actual search results:
Example 1.30.
@Name("searchResults")
public class SearchService
{
@In(create=true)
private EntityManager entityManager;
@RequestParameter
private String searchPattern;
private List<BlogEntry> searchResults;
@Create
public void initSearchResults()
{
searchResults = entityManager.createQuery("from BlogEntry be where lower(be.title) like :searchPattern or lower(be.body) like :searchPattern order by be.date desc")
.setParameter( "searchPattern", getSqlSearchPattern() )
.setMaxResults(100)
.getResultList();
}
private String getSqlSearchPattern()
{
return searchPattern==null ? "" : '%' + searchPattern.toLowerCase().replace('*', '%').replace('?', '_') + '%';
}
@Unwrap
public List<BlogEntry> getSearchResults()
{
return searchResults;
}
}Very occasionally, it makes more sense to use push-style MVC for processing RESTful pages, and so Seam provides the notion of a page action. The Blog example uses a page action for the blog entry page, entry.xhtml. Note that this is a little bit contrived, it would have been easier to use pull-style MVC here as well.
The entryAction component works much like an action class in a traditional push-MVC action-oriented framework like Struts:
Example 1.31.
@Name("entryAction")
@Scope(ScopeType.STATELESS)
public class EntryAction
{
@In(create=true)
private Blog blog;
@RequestParameter
private String blogEntryId;
@Out(scope=ScopeType.EVENT, required=false)
private BlogEntry blogEntry;
public void getBlogEntry()
{
blogEntry = blog.getBlogEntry(blogEntryId);
if (blogEntry==null)
{
HttpError.instance().send(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND);
}
}
}The page action must be declared a file called pages.xml:
Example 1.32.
<pages>
<page view-id="/entry.xhtml" action="#{entryAction.getBlogEntry}"/>
<page view-id="/post.xhtml" action="#{loginAction.challenge}"/>
<page view-id="*" action="#{blog.hitCount.hit}"/>
</pages>(Notice that the example is using page actions for some other functionality—the login challenge, and the page counter.)
When the entry.xhtml page is requested, Seam first runs the page action, which retrieves the needed data—the blogEntry—and places it in the Seam event context. Next, the following is rendered:
Example 1.33.
<div class="blogEntry">
<h3>#{blogEntry.title}</h3>
<div>
<h:outputText escape="false" value="#{blogEntry.body}"/>
</div>
<p>
[Posted on
<h:outputText value="#{blogEntry.date}">
<f:convertDateTime timezone="#{blog.timeZone}" locale="#{blog.locale}" type="both"/>
</h:outputText>]
</p>
</div>