What Is a JSP Page? - The J2EE 1.4 Tutorial
What Is a JSP Page?
A JSP page is a text document that contains two types of text: static data, which can be expressed in any text-based format (such as HTML, SVG, WML, and XML), and JSP elements, which construct dynamic content.
The recommended file extension for the source file of a JSP page is
.jsp. The page can be composed of a top file that includes other files that contain either a complete JSP page or a fragment of a JSP page. The recommended extension for the source file of a fragment of a JSP page is.jspf.The JSP elements in a JSP page can be expressed in two syntaxes--standard and XML--though any given file can use only one syntax. A JSP page in XML syntax is an XML document and can be manipulated by tools and APIs for XML documents. This chapter and Chapters 14 through 16 document only the standard syntax. The XML syntax is covered in Chapter 13. A syntax card and reference that summarizes both syntaxes is available at
Example
The web page in Figure 12-1 is a form that allows you to select a locale and displays the date in a manner appropriate to the locale.
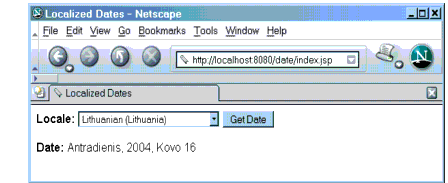
Figure 12-1 Localized Date Form
The source code for this example is in the
<INSTALL>/j2eetutorial14/examples/web/date/directory. The JSP page,index.jsp, used to create the form appears in a moment; it is a typical mixture of static HTML markup and JSP elements. If you have developed web pages, you are probably familiar with the HTML document structure statements (<head>,<body>, and so on) and the HTML statements that create a form (<form>)and a menu (<select>).The lines in bold in the example code contain the following types of JSP constructs:
- A page directive (
<%@page ... %>) sets the content type returned by the page.- Tag library directives (
<%@taglib ... %>) import custom tag libraries.jsp:useBeancreates an object containing a collection of locales and initializes an identifier that points to that object.- JSP expression language expressions (
${ }) retrieve the value of object properties. The values are used to set custom tag attribute values and create dynamic content.- Custom tags set a variable (
c:set), iterate over a collection of locale names (c:forEach), and conditionally insert HTML text into the response (c:if,c:choose,c:when,c:otherwise).jsp:setPropertysets the value of an object property.- A function (
f:equals) tests the equality of an attribute and the current item of a collection. (Note: A built-in==operator is usually used to test equality).Here is the JSP page:
<%@page contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" %> <%@tagliburi="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> <%@tagliburi="/functions" prefix="f" %> <html> <head><title>Localized Dates</title></head> <body bgcolor="white"> <jsp:useBeanid="locales" scope="application" class="mypkg.MyLocales"/> <form name="localeForm" action="index.jsp" method="post"> <c:setvar="selectedLocaleString" value="${param.locale}" /> <c:setvar="selectedFlag" value="${!empty selectedLocaleString}" /> <b>Locale:</b> <select name=locale> <c:forEachvar="localeString" items="${locales.localeNames}" > <c:choose> <c:whentest="${selectedFlag}"> <c:choose> <c:whentest="${f:equals(selectedLocaleString, localeString)}" > <option selected>${localeString}</option> </c:when> <c:otherwise> <option>${localeString}</option> </c:otherwise> </c:choose> </c:when> <c:otherwise> <option>${localeString}</option> </c:otherwise> </c:choose> </c:forEach> </select> <input type="submit" name="Submit" value="Get Date"> </form> <c:iftest="${selectedFlag}" > <jsp:setPropertyname="locales" property="selectedLocaleString" value="${selectedLocaleString}" /> <jsp:useBeanid="date" class="mypkg.MyDate"/> <jsp:setPropertyname="date" property="locale" value="${locales.selectedLocale}"/> <b>Date: </b>${date.date}</c:if> </body> </html>A sample
date.waris provided in<INSTALL>/j2eetutorial14/examples/web/provided-wars/. To build this example, perform the following steps:To package and deploy the example using
asant, follow these steps:To learn how to configure the example, use
deploytoolto package and deploy it:
- Start the Application Server.
- Start
deploytool.- Create a web application called
dateby running the New Web Component wizard. Select FileNew
Web Component.
- In the New Web Component wizard:
- Select the Create New Stand-Alone WAR Module radio button.
- In the WAR File field, enter
<INSTALL>/docs/tutorial/examples/web/date/date.war. The WAR Display Name field showsdate.- In the Context Root field, enter
/date.- Click Edit Contents.
- In the Edit Contents dialog box, navigate to
<INSTALL>/j2eetutorial14/examples/web/date/build/. Selectindex.jsp,functions.tld, and themypkgdirectory and click Add, then click OK.- Click Next.
- Select the No Component radio button, then click Next.
- Click Finish.
- Select File
Save.
- Deploy the application.
To run the example, perform these steps:
You will see a combo box whose entries are locales. Select a locale and click Get Date. You will see the date expressed in a manner appropriate for that locale.
